Emulated network adapters
A VM contains emulated network adapters which are connected to virtual switches (vSwitches). All the VMs whose adapters connect to the same vSwitch form a subnet and use it to communicate with each other. The subnets are isolated from each other but may be interconnected by using a VM as a router or bridge.
A virtual switch (vSwitch) is just a piece of software which exists on the host and separates the virtual network from the physical one. A bridge protocol provides the uplink to the LAN and tunnels traffic through the vSwitch via physical network cards if required. Whether a guest system remains isolated or can communicate with physical machines depends on the configuration of the vSwitch.
The VMWare server provides up to four virtual network cards for each VM. The user can assign or remove these via "VM –> Settings –> Hardware". Independently of the actual hardware installed, the software fully emulates every NIC. In a test environment, VMs can even exchange data across virtual networks without any physical adapters at all.
VMware is factory-set to emulate an AMD PCNet adapter, and almost every operating system provides drivers for this adapter. Due to plug & play technology, the guest system automatically installs the driver as if it were an actual hardware component. All the protocols, for example TCP/IP or IPX]/SPX, work as usual. If VMware tools are installed on the guest system they replace the standard driver with an optimised "VMware Accelerated AMD PCNet Adapter". It offers better performance for Gigabit Ethernet and takes pressure off the host CPU. In 64-bit guests, VMware also emulates an Intel PRO/1000 adapter for which a 64-Bit driver is available in many guest operating systems.
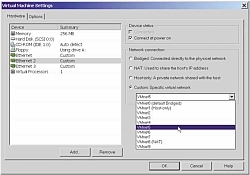
![]() Network selection: via the VM settings, admins can link "Ethernet" virtual network cards with "VMnet" virtual networks
Network selection: via the VM settings, admins can link "Ethernet" virtual network cards with "VMnet" virtual networks
Incidentally, the guest's LAN speed is displayed for purely cosmetic reasons. It will only ever read 10 MBit/s with the standard driver, even though the system will use the speed available through the physical connection. The optimised driver, on the other hand, always reads 1GBit/s, even if the physical link only manages 100MBit/s.
To connect the VM adapters to each other, VMware supplies a total of ten virtual switches called VMnet0 to VMnet9. A virtual adapter can be connected via the "VM –> Settings –> Hardware" menu or more simply by clicking on the small network symbol in the status bar of a running VM. VMnets can be reassigned and adapters can be connected or disconnected during operation - for the guest system, this is equivalent to re-plugging a patch cable.




![Kernel Log: Coming in 3.10 (Part 3) [--] Infrastructure](/imgs/43/1/0/4/2/6/7/2/comingin310_4_kicker-4977194bfb0de0d7.png)

![Kernel Log: Coming in 3.10 (Part 3) [--] Infrastructure](/imgs/43/1/0/4/2/3/2/3/comingin310_3_kicker-151cd7b9e9660f05.png)












